
Find out more about our approach to stress fracture treatment. Treatment for stress fractures ranges from rest to physical therapy. Read more about stress fracture diagnosis at Stanford. Diagnosing Stress FracturesĪ physical examination helps us confirm a stress fracture. Learn more about stress fracture symptoms. Some people may experience swelling as well. The most common symptom of a stress fracture is pain in the foot. The bones in the midfoot (metatarsals) in runners are especially vulnerable to stress fractures. Stress fractures often occur in the foot after training for basketball, running, and other sports. Stress fractures are weak spots or small cracks in the bone caused by continuous overuse.
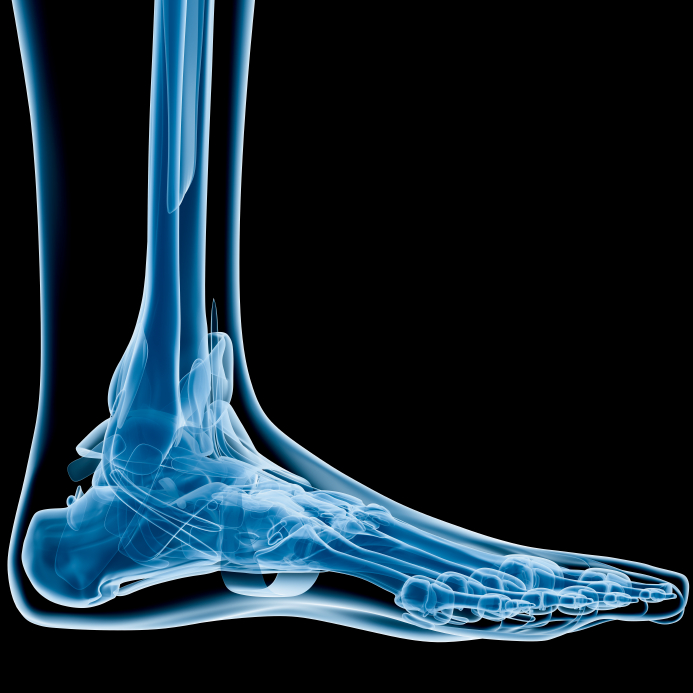
Surgery may be required if the fracture is not healed completely by non-surgical treatment. Crutches may be used to prevent the weight on the foot until the stress fracture is healed completely. Your doctor may apply a cast to the foot to immobilize the leg which also helps to remove the stress. Protective footwear may be recommended which helps to reduce stress on the foot. Re-injury can also occur without allowing the stress fracture to completely heal. If children return too quickly to the activity that has caused a stress fracture, it may lead to chronic problems such as harder-to-heal stress fractures. Stress fractures can be treated by non-surgical approach which includes rest and limiting the physical activities that involve Foot & Ankle. Treatment of Stress Fractures Non-Surgical Method Some of the diagnostic tests such as X-ray, MRI scan or bone scan may be required to confirm the fracture. Your doctor will diagnosis the condition after discussing symptoms and risk factors and examines the Foot & Ankle. Swelling, bruising, and tenderness may also occur at a specific point.

The most common symptom is a pain in the foot which usually gets worse during exercises and decreases upon resting. The risk of developing stress fracture increases in females if the bone weight decreases. It is a combination of eating disorders, amenorrhea (irregular menstrual cycle), and osteoporosis (thinning of the bones). These tiny cracks in your bones develop when your muscles become overtired (fatigued) and can no longer. An athlete with inadequate rest between workouts can also develop stress fracture.įemales are at a greater risk of developing stress fracture than males, and may be related to a condition referred to as “female athlete triad”. Stress fractures are a type of overuse injury.
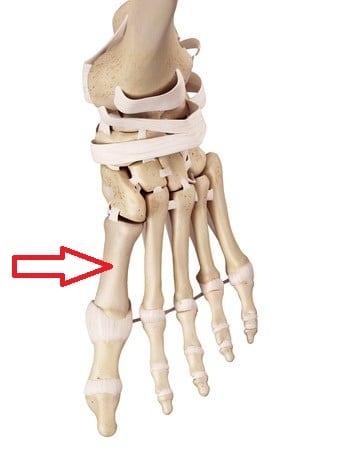
During these sports the repetitive stress of the foot strike on a hard surface causing trauma and muscle fatigue. They can also be caused by impact on a hard surface, improper footwear, and increased physical activity.Īthletes participating in certain sports such as basketball, tennis or gymnastics are at a greater risk of developing stress fractures. Stress fractures are caused by a rapid increase in the intensity of exercise. When the muscles of the foot are overworked or stressed, they are unable to absorb the stress and when this happens the muscles transfer the stress to the bone which results in stress fracture. It commonly develops in the weight-bearing bones of the lower leg and foot.
Stress fracture in foot symptoms crack#
A stress fracture is described as a small crack in the bone which occurs from an overuse injury of a bone.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
